FAQs About Anxiety and Panic Disorders
What Is the Difference Between Anxiety and an Anxiety Disorder?
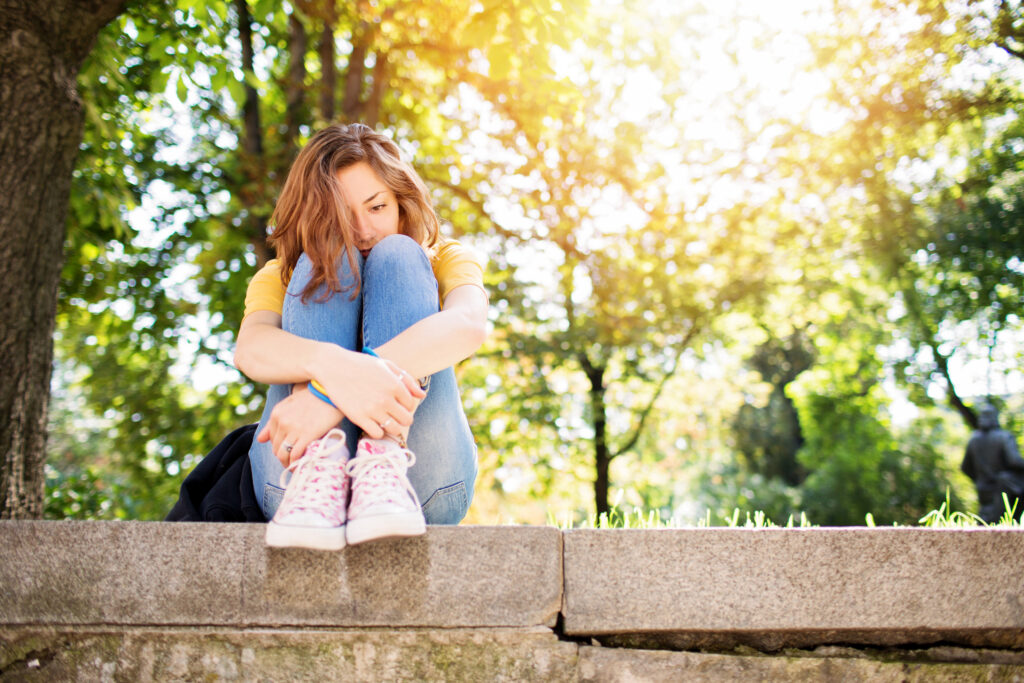
Almost everyone experiences feelings of anxiety at some point, but an anxiety disorder involves excessive and persistent worry or fear that interferes with daily life and functioning. Common anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Social anxiety
- Panic disorder
- Phobias.
How Do I Know if I’m Having a Panic Attack?
Panic attacks are characterized by a sudden onset of intense fear or discomfort that peaks within minutes. Symptoms may include heart palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling, sweating, nausea, dizziness and feelings of unreality or fear of losing control. While panic attacks are very frightening, they are not life-threatening.
Can Anxiety Disorders Be Cured?
While there is no definitive cure, anxiety disorders are highly treatable. A combination of psychotherapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy) and medication (if recommended by a provider) can provide significant relief from symptoms and help patients develop coping strategies
What Causes Someone to Develop an Anxiety Disorder?
Anxiety disorders likely result from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors such as stressful life events, trauma, or learned behaviors and thought patterns. Brain chemistry also plays a role.
At What Age Do Anxiety Disorders Typically Begin?
Anxiety disorders can start at any age, but many develop during childhood, adolescence or early adulthood years. The median age of onset is 11 years old. Prompt treatment is important, as untreated anxiety disorders tend to persist into adulthood.